Visualizing Conv filters using ActivationMaximization
Preparation
Load libraries
[1]:
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from packaging.version import parse as version
from tf_keras_vis.utils import num_of_gpus
if version(tf.version.VERSION) < version('2.16.0'):
import tensorflow.keras as keras
else:
import keras
_, gpus = num_of_gpus()
print('Tensorflow recognized {} GPUs'.format(gpus))
2025-03-12 12:14:30.711256: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:477] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered
WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR
E0000 00:00:1741749270.734787 1580 cuda_dnn.cc:8310] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered
E0000 00:00:1741749270.738998 1580 cuda_blas.cc:1418] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
2025-03-12 12:14:30.756316: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:210] This TensorFlow binary is optimized to use available CPU instructions in performance-critical operations.
To enable the following instructions: AVX2 AVX512F AVX512_VNNI FMA, in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
Tensorflow recognized 0 GPUs
2025-03-12 12:14:34.860354: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_driver.cc:152] failed call to cuInit: INTERNAL: CUDA error: Failed call to cuInit: CUDA_ERROR_NO_DEVICE: no CUDA-capable device is detected
Load keras.Model
In this notebook, we use VGG16 model, however if you want to use other keras.Model, you can do so by modifying the section below.
[2]:
model = keras.applications.vgg16.VGG16(weights='imagenet', include_top=True)
model.summary()
Model: "vgg16"
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ ┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃ ┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩ │ input_layer (InputLayer) │ (None, 224, 224, 3) │ 0 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block1_conv1 (Conv2D) │ (None, 224, 224, 64) │ 1,792 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block1_conv2 (Conv2D) │ (None, 224, 224, 64) │ 36,928 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block1_pool (MaxPooling2D) │ (None, 112, 112, 64) │ 0 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block2_conv1 (Conv2D) │ (None, 112, 112, 128) │ 73,856 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block2_conv2 (Conv2D) │ (None, 112, 112, 128) │ 147,584 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block2_pool (MaxPooling2D) │ (None, 56, 56, 128) │ 0 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block3_conv1 (Conv2D) │ (None, 56, 56, 256) │ 295,168 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block3_conv2 (Conv2D) │ (None, 56, 56, 256) │ 590,080 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block3_conv3 (Conv2D) │ (None, 56, 56, 256) │ 590,080 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block3_pool (MaxPooling2D) │ (None, 28, 28, 256) │ 0 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block4_conv1 (Conv2D) │ (None, 28, 28, 512) │ 1,180,160 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block4_conv2 (Conv2D) │ (None, 28, 28, 512) │ 2,359,808 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block4_conv3 (Conv2D) │ (None, 28, 28, 512) │ 2,359,808 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block4_pool (MaxPooling2D) │ (None, 14, 14, 512) │ 0 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block5_conv1 (Conv2D) │ (None, 14, 14, 512) │ 2,359,808 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block5_conv2 (Conv2D) │ (None, 14, 14, 512) │ 2,359,808 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block5_conv3 (Conv2D) │ (None, 14, 14, 512) │ 2,359,808 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ block5_pool (MaxPooling2D) │ (None, 7, 7, 512) │ 0 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ flatten (Flatten) │ (None, 25088) │ 0 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ fc1 (Dense) │ (None, 4096) │ 102,764,544 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ fc2 (Dense) │ (None, 4096) │ 16,781,312 │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ predictions (Dense) │ (None, 1000) │ 4,097,000 │ └─────────────────────────────────┴────────────────────────┴───────────────┘
Total params: 138,357,544 (527.79 MB)
Trainable params: 138,357,544 (527.79 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 B)
Implement functions required to use ActivationMaximization
Model modifier
You MUST define a model modifier to replace the model output to target layer’s output that has filters you want to visualize, and , in addion, replace the function of it to a linear activation function.
Although we create and use ExtractIntermediateLayer and ReplaceToLinear instance, we can also use the model modifier function defined by ourselves.
[3]:
from tf_keras_vis.utils.model_modifiers import ExtractIntermediateLayer, ReplaceToLinear
layer_name = 'block5_conv3' # The target layer that is the last layer of VGG16.
# This instance constructs new model whose output is replaced to `block5_conv3` layer's output.
extract_intermediate_layer = ExtractIntermediateLayer(index_or_name=layer_name)
# This instance modify the model's last activation function to linear one.
replace2linear = ReplaceToLinear()
# Instead of using ExtractIntermediateLayer and ReplaceToLinear instance,
# you can also define the function from scratch as follows:
def model_modifier_function(current_model):
target_layer = current_model.get_layer(name=layer_name)
target_layer.activation = keras.activations.linear
new_model = keras.Model(inputs=current_model.inputs, outputs=target_layer.output)
return new_model
Score function
And then, you MUST create Score instance or define score function that returns target scores. Here, they return the value of 3rd filter in block5_conv3 layer.
[4]:
from tf_keras_vis.utils.scores import CategoricalScore
filter_number = 3
score = CategoricalScore(filter_number)
# Instead of using CategoricalScore object above,
# you can also define the function from scratch as follows:
def score_function(output):
return output[..., filter_number]
Visualizeing a conv filter
Create ActivationMaximization Instnace
When clone argument is True(default), the model will be cloned, so the model instance will be NOT modified, however the process may take a while.
Here, because the ExtractIntermediateLayer instance will construct new model, setting False.
[5]:
from tf_keras_vis.activation_maximization import ActivationMaximization
activation_maximization = ActivationMaximization(
model,
# Please note that `extract_intermediate_layer` has to come before `replace2linear`.
model_modifier=[extract_intermediate_layer, replace2linear],
clone=False)
Visualize
ActivationMaximization will maximize the value computed by the score function. Here, we will visualize the 63rd convolutional filter.
[6]:
%%time
from tf_keras_vis.activation_maximization.callbacks import Progress
# Generate maximized activation
activations = activation_maximization(score, callbacks=[Progress()])
activations = activations.astype(np.uint8)
# Render
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(4, 4))
ax.imshow(activations[0])
ax.set_title('filter[{:03d}]'.format(filter_number), fontsize=16)
ax.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
200/200 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 131s 655ms/step - Score: 383.8325 - TotalVariation2D: 10.1696 - Norm: 38.4541

CPU times: user 10min 9s, sys: 39.7 s, total: 10min 48s
Wall time: 2min 11s
Visualizing Conv filters
Then, let’s visualize multiple convolutional filters!
Modify Score function
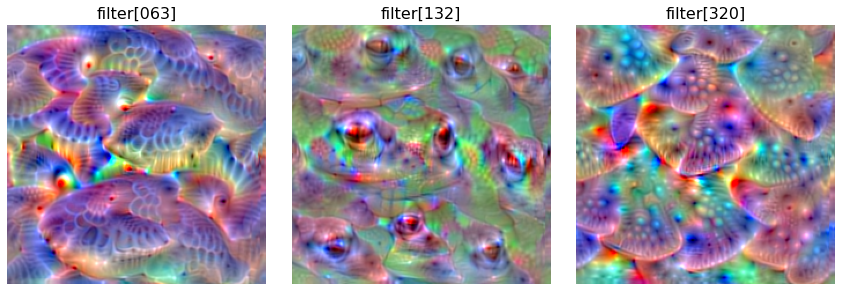
Because change the target you want to visualize, you MUST create Score instance or define score function again. Here, our socre function returns the values corresponding to 63rd, 132nd and 320th filters of the layer.
[7]:
from tf_keras_vis.utils.scores import CategoricalScore
filter_numbers = [63, 132, 320]
scores = CategoricalScore(filter_numbers)
Create Seed-Input values
And then, you MUST create seed_input value. In default, when visualizing a specific filter, tf-keras-vis automatically generates seed_input to visualize a image. When visualizing multiple images, you MUST manually create seed_input.
[8]:
# Define seed inputs whose shape is (samples, height, width, channels).
seed_input = tf.random.uniform((3, 224, 224, 3), 0, 255)
Visualize
[9]:
%%time
from tf_keras_vis.activation_maximization.callbacks import Progress
# Generate maximized activation
activations = activation_maximization(scores, seed_input=seed_input, callbacks=[Progress()])
activations = activations.astype(np.uint8)
# Render
f, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(12, 4))
for i, filter_number in enumerate(filter_numbers):
ax[i].set_title('filter[{:03d}]'.format(filter_number), fontsize=16)
ax[i].imshow(activations[i])
ax[i].axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
200/200 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 358s 2s/step - Score: 403.1880 - TotalVariation2D: 10.4963 - Norm: 38.4931
CPU times: user 33min 48s, sys: 1min 30s, total: 35min 18s
Wall time: 5min 58s
